How to ensure better results from an IT team in your projects? You probably already know that this management can be extremely challenging, especially if there is no good planning and an efficient approach is not used.
Deadlines can be extended too much, costs become uncontrolled, and there is a risk that the final product will not please the customer and not meet the requirements. Unexpected problems occur and disrupt the flow.
Thinking about these problems, some professionals in the area met to systematize a set of principles called agile project management methodologies. The focus is to generate agility, flexibility and adapt teams well to the dynamic demands of the modern world, providing innovation.
If you want to learn more about it in order to improve your processes and get agility in operations, follow the article.
How does agile project management work?
As we said in the introduction, maintaining IT project demands is not easy. Currently, a number of internal and external factors can disrupt operations and generate errors that accumulate in production. For managers, it is always the responsibility to please customers even with all these difficulties.
Some classic problems of software creation processes are the poor definition of deadlines, poor adaptation to changes, the rigidity of methods and documentation, implications of crises, as well as other factors. For years, this was the reality of many designers and team members in the area.
It is easy to understand that a development full of sensitive issues like these does not remain consistent in today’s world. Today, technologies change very fast; new trends arise and it is often necessary to reassess decisions taken previously.
Sometimes a programming pattern or framework has been defined in planning, however new, more effective options appear on the market and require adaptation.
Agile management then employs a new mindset for project management, seeking to generate flexibility, agility, collaboration, and error reduction. It is based on dividing large problems into smaller parts, following the famous principle of “divide to conquer”. Similarly, it focuses heavily on sharing information and roles in order to create greater synergy among members.
Continuous deliveries
Another issue very characteristic of agile methods: continuous deliveries, with feedback and active collaboration of customers. That is, development is now divided into small sections, with results at the end of each. The purpose of these deliveries is precisely to produce value for contractors and gain insights in order to adjust the product later.
To meet this, even, infrastructure and development teams are integrating more in order to meet the same objectives. In this sense, DevOps and derivations emerged, such as DataOps, which consists of better communication between data analysis personnel and the operations team.
Iterative Phases
Because of this, the production phases are Iterative and dynamic, unlike a more rigid flow, such as the one before. That is, the team can always go back to previous steps in order to adjust some points and improve the result.
An example of this is the test phase that can be run at any time whenever there is a demand for changes from customers.
In general, we can summarize agile project management methodologies as being extremely focused on people, delivering functional results, prioritizing adaptation to changes, and dialoguing with the client throughout the process, making him a part of the team practically.
What are the main methodologies of agile project management?
We will now understand how these principles converge on the main tools used in the market.
Scrum
Scrum is one of the most famous and robust strategies. It consists, initially, of adopting a new vocabulary: terms such as product backlog and scrum master are commonly used in daily life.
The product backlog concerns the set of core features, that is, requirements with a more complete description. Whereas the scrum master is the team leader who specifically manages the processes and steps of the methodology.
Each development phase that results in functional deliveries is called a sprint. Each sprint has a backlog with the activities that must be developed in it. Scrum states that there should be periodic meetings after sprints to readjust the project.
We also have the product owner, who is representative of the customer’s interests within the team, being responsible for directing the flow and focus of production at each stage.
XP
XP, or eXtreme Programming, is a programming-focused method that prioritizes cost savings, simplicity, product quality and consistency, and process agility. To do this requires daily meetings and more general alignment meetings in order to get ideas for incremental change and continuous improvement.
FDD
FDD is Feature Driven Development, which means feature-oriented development. That is, its main focus is to divide large tasks and programs into small parts that perform certain services.
Ideally, each team member is responsible for only one of the parties and that these smaller blocks are continuously integrated.
In addition, FDD prescribes more general principles that also appear in the rules of other methods, such as quality control at all stages and focus on testing.
DSDM
The DSDM, or Dynamic System Development Model, is focused on projects with fixed costs and tight deadlines. It is somewhat different from other frameworks because it does not make time management more flexible. Even if they are open to incremental changes, everything must be done with the same periods stipulated for execution.
Lean
Lean is a management method that prioritizes efficiency, above all. The term is translated as “lean”, precisely by seeking a project version that is as costly and time-consuming as possible. Thus, it is an optimal methodology for those seeking cost reduction and continuous improvement, both of the processes and of the final product.
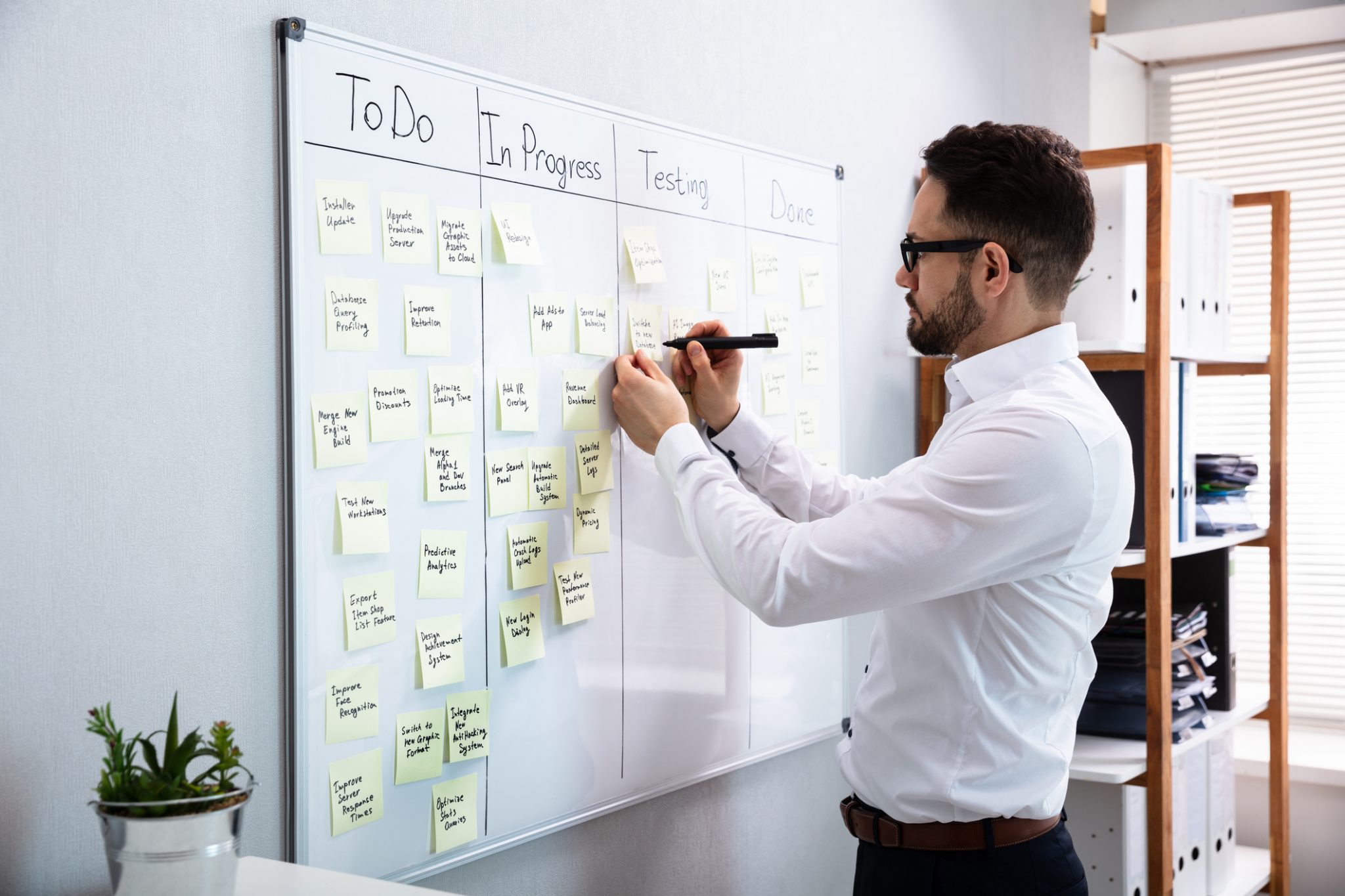
Kanban
Kanban is a management method that seeks to divide tasks in order of priority and importance, according to their status. Thus, it is possible to better deal with possible problems that occur in the operational flow. The steps are: “to do”, “doing” and “done”.
Kanban must be visually orchestrated to cause team alignment and optimize transparency with respect to what is being done and what will be done. In this sense, a set of post-its or specific software can be used.
How to monitor results?
The implementation of agile methodologies depends on some later stages of analysis and adjustment. After all, since the company is already operating with the help of these tools, it is necessary to evaluate whether the methods are working as expected and are yielding good results.
In this sense, project management software is essential. It helps you track the most relevant indicators and understand whether performance is being satisfactory or not with easy-to-understand numbers.
Thus, it is possible to adjust what is bad and obtain continuous improvements in processes in order to result in better phases, fewer costs, and greater alignment in development journeys.
Agile project management methodologies are strategies that aim to revolutionize the way companies approach development stages. Thus, it is possible to obtain greater collaboration, flexibility, agility, and adaptation to changes in order to generate value for contractors and reduce errors. At the same time, it is the key to innovation.
Did you like it? Understand more about the importance of agile methodologies.